Building a Multidisciplinary Discourse – the Way to the High-Technology Future of the Planet. Silver medal
Almanac: Kondratieff waves:Processes, Cycles, Triggers, and Technological Paradigms
DOI: https://doi.org/10.30884/978-5-7057-6191-3_07
The global multifactorial hybrid crisis, which is taking place today, will only intensify, adapting people and their potential to themselves. The high-tech revolution (digital developments, artificial intelligence, etc.) will change a human. In addition, it is necessary to counteract the depletion of natural resources and to maintain the planet's eco-balance, but in an attempt to find the trajectory of sustainable space exploration (as an intermediate super-task).
However, ‘for the transition from quantity to quality’, interdisciplinary research links are needed, when there are identified the key system-forming principles of life / nature (world-system analysis), which can be used for the solution to the above problems. One of them is the cyclical / wavelike principle of building life. The author gives some examples, covering the quantum level, ‘large spaces’ and the socio-humanitarian layer.
Keywords: waves and cycles of global development, hybrid crisis, converging technologies of the NBIC and NBICS groups, natural sciences, artificial intelligence, world-system analysis.
The current moment is unique in its depth. A multifactorial hybrid crisis is unfolding before our eyes, combining not only the growing financial and economic imbalances in the global economy (also of an essentially unprecedented scale, exceeding the size of the very powerful shock of 2008–2009), but also colossal information flows (hence psychological problems, digital dementia), intensification of geopolitical clashes (both diplomatic and military, including acute open conflicts), as well as educational, moral and ethical crises, and now also the COVID-19 coronavirus pandemic with all the far-reaching consequences.
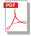
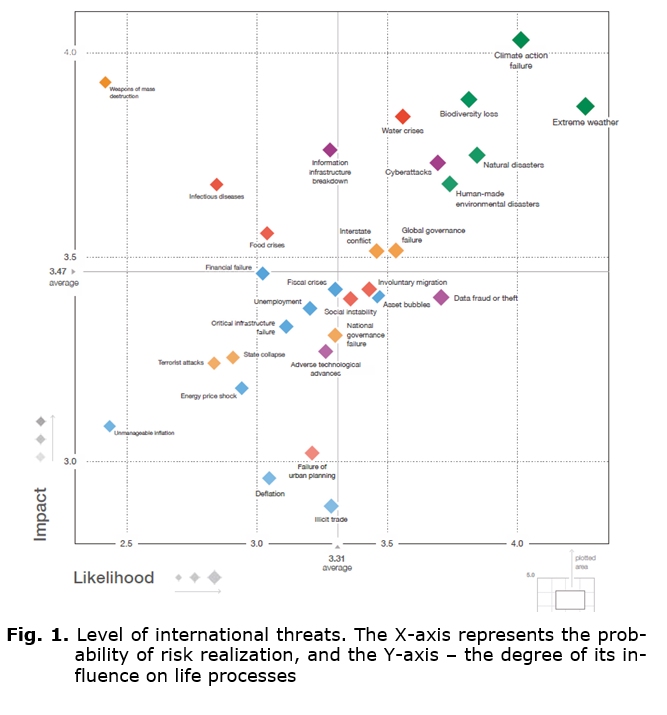
In this regard, it is noteworthy that the experts of the World Economic Forum (WEF) in Davos (World Economic Forum n.d.) annually publish the results of their research in the form of a forecast of global risks for all mankind – Global Risk Report. Moreover, their number is growing steadily every year (The Global Risks Report 2019, 2020). Among the new challenges, they are increasingly emphasizing the fact that the high dynamics of technology development is associated with a constant increase in the corresponding high-tech risks, key among which are the insecurity of the digital environment and the threat of cyber-attacks (see Fig. 1 and Table).
Yet at the heart of the technological revolution lies another fundamental hu-man vulnerability. Any technology is a ‘prosthesis’ that enhances / increases human capabilities (and subsequently replaces them). Therefore, the expected large-scale merger with our life of various developments that simplify our life will actually complement a human with various such ‘prostheses’, such as artificial intelligence, information and telecommunication technologies, virtual and augmented reality, robotics, ‘smart’ home, etc. All this will change a human and adapt his potential to itself (Smirnov 2011). These technologies will improve people, but at the same time will sharply raise the problem of the loss of their identity – it is already happening, manifesting itself in the growth of Internet addiction, especially among young people.
Such crisis dynamics, its predicted manifold deterioration require qualitatively different approaches or strategies capable of offering a commensurate and adequate response. Therefore, the legacy of Nikolai Kondratieff is more relevant today than ever. It is probably fair to say that the best confirmation of the scholar's merits is how long his ideas live, and in the case of Kondratieff, this speaks for itself. Among other things, this world-known scholar, in fact, revealed the fundamental principle on which life is built – the cycles and waves of global development.
Today, the understanding of such processes is also very important because a new full-scale wave of high-tech world economic order which should radically change the life we are used to is unfolding (Glazyev 2018). And the choice, based on this option – the merging of a human with the technosphere and increasing dependence on it, on the one hand, or making a new reality for the benefit of humanity without artificial transformation of human nature, on the other hand, becomes relevant and decisive precisely today, when we are still at the beginning of this path.
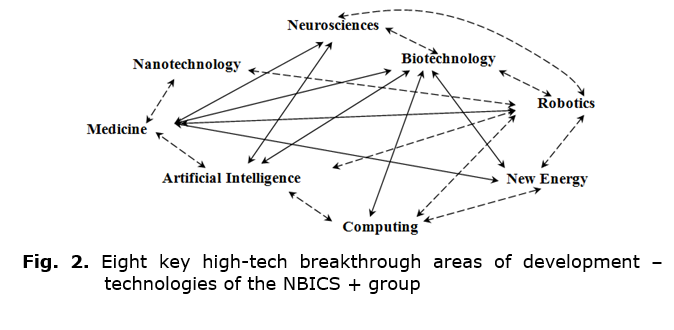
In such a context, it is important to draw a clear distinction between the two fundamental groups of convergent technologies – NBIC and NBICS (nano-, bio-, info-, cogno-, socio-), which represent the number of developments that,
if properly implemented, can generally replace a human (Smirnov 2018).
NBIC vs NBICS
It is necessary to realize the essence of the clear distinction between the crisis dynamics of the global trend of the world development, which is exacerbated by the advancement of the NBIC critical technologies group, and the incipient movement that, in fact, would be able to preserve the biosphere of our planet and a human in it through the use of nature-like technologies based on a group of convergent technologies (NBICS).
At present leading high-tech Western countries focus on the sixth wave of the technological paradigm, the key developments of which are NBIC technologies, which together ensure the reproduction of an artificially created human:
N (nano-) – nanotechnology enabling an unprecedented minimization of the mechanics of processes;
B (bio-) – bioengineering and biomedicine, providing the synthesis of living things and materials;
I (info-) – information technology, that is, the entire information environment;
C (cogno-) – artificial intelligence, related processes to achieve intelligent data processing.
The general global trend of the formation of a new technological paradigm is that when improving new technologies there appear the systems that in the production of goods and services necessary and sufficient for the effective operation of the ruling class exclude the human presence in them. When necessary, he may be connected to electronic external control systems. It is assumed that robots with artificial intelligence will replace humans and this will lead to the creation of a more managed economic system. Already by 2024–2025 the elements of computer intelligence will become compulsory in cars, and in the future people will be prohibited from driving a car not equipped with such computer assistants. Thus, there will be a loss of human significance as a subject of the future economy, and this implies a number of very disappointing consequences.
It is noteworthy that in 2009, in order to train relevant personnel – potential leaders who contribute to the advancement of ‘technologies for solving global problems of mankind’, the Singularity University[1] located in Silicon Valley was created.
Technological singularity is the point in time when machines will begin to improve themselves and without outside help (estimated by 2045). This is exacerbated by an unprecedented growth of the rate of world economic processes, owing also to the fact that the maximum Internet bandwidth by 2041 will be 500 million times more than today. By 2039, nano-devices will be implanted directly into the brain and will randomly input and output signals from brain cells. This will lead to a full immersion virtual reality that does not require any additional equipment.
A team at Singularity University is currently working on a computer that can reproduce the human nervous system. For this purpose, the computer is ‘trained’ to understand natural language and semantic text. Since the production of the new machine requires data on each of the two billion internet users, Google, the co-founder of Singularity University, appeared to be the perfect partner. It is assumed that as a result of such experiments, the system will know at a semantically deep level everything that a modern consumer is interested in, and not just the main topics of his interests. As a result, there will take place such a fusion of humans with a computer, in which the initiative will imperceptibly come from the computer, which, under the guise of ‘guessing’, will form and direct the interests of a human.
Thus, based on the analysis of only the intellectual fragment of the NBIC group technologies, one can assume that they, as closing technologies in their content, will largely determine the contours of the further evolution of all mankind. Moreover, this means not only the way of life, communication, the speed of information exchange and decision-making, but also a deeper level, involving the transformation of the collective consciousness of a modern urban human. These technologies can greatly distort human nature, in particular, through the artificial life extension or various experiments with self-organizing living matter.
Bionic man is, on the one hand, the robotization of the human, that is, the introduction of artificial implants or chips into the body and brain and, on
the other hand, the creation of humanoid android robots. Achieving immortality becomes theoretically possible through the use of biotechnology (stem cells, cloning, cryonics) and information and nano-technologies (‘downloading consciousness’), which implies a complete copying of the human brain on a computer. The idea is to electronically carry out the same computations that occur in the brain's neural network after scanning the brain structures (Moravec 1988).
Such an NBIC surrogate is dangerous because it gains access to a colossal amount of information circulating and multiplying in the global network. Google alone processes more than 25 petabytes of data every day (one petabyte equals one million gigabytes). Moreover, thanks to the achievements of artificial intelligence and neural networks, such a system constantly learns itself.
The further development will lead to ‘cloud robotics’ which is as follows. A robot connected to the cloud has access to vast amounts of data and shared experiences from other devices, with which it can improve its understanding of its own beliefs. Before cloud connectivity became possible, the robot's dataset was limited – it consisted of either its own experience or the knowledge of a small group of robots. However, at present being connected to the network and staying connected to the cloud at all times, robots can use the experience of any other robot, learning at an accelerated pace. Imagine something like the quantum leap that human culture would make if we were all suddenly able to directly connect to the knowledge and experience of all people of the world. Big Data has made this quantum leap possible in the cognitive development of robots.
Russian scientists of the National Research Center ‘Kurchatov Institute’, which under the leadership of Professor, Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences Mikhail Kovalchuk are developing technologies of a new technological paradigm, additionally include social technologies (NBICS) in their list. In contrast to the global trend, in Russia the creation of a new technological paradigm is aimed at the development of society, and, therefore, at the development of each human. Therefore, the basis for the creation of all technologies is the principle of reproduction of nature-like systems that ensure the preservation of a natural highly ecological human environment and human species. This is exactly what the President of the Russia Vladimir Putin said from the rostrum of the UN General Assembly in September 2015, when he called on the international community to create nature-like technologies to prevent environmental problems associated with global climate change on Earth.
Thus, the intellectual semantics of the group of technologies is radically changing – from NBIC to NBICS, that is, from a tendency towards the technologization of human space with the entire palette of the above risks – to a smart anthropogenic and socially oriented approach. The implementation of such an intention within the framework of the development of the ecological component is able to adjust the world development, chanelling it towards the care for traditional human values, halting the destruction of the Earth and restoring the role of natural processes in preserving the ecosystem of our planet and human species in his natural state (Smirnov and Golovkov 2017; Go-lovkov and Smirnov 2017).
Depending on the result of the implementation of these two groups of technologies, completely different technological paradigms of society are expected.
On the Question of ‘NBICS +’
Over time, the NBICS group will become NBICS + (Smirnov 2018). Firstly, ‘+’ are those technologies, which significantly affect the transformation of the world. So, these are distributed ledger technologies, for example, blockchain (Genkin and Mikheev 2018) and ‘smart contracts’ derived from it (this is explained by the transfer of financial, economic and production processes, as well as the service sector to the digital domain). It is also any technology that can start the process of changing technological paradigms. Secondly, this is a set of technologies that allows us to talk about the phase of transition of all mankind to the area of qualitatively different tasks aimed at expanding the habitat of mankind to the next stage – to the borders of the solar system. This aspect is probably the most fundamental for the future of all mankind, since it not only expands the scope of scientists' thinking, but also ensures the sustainable development of nature-like science, which will work to ensure such a large-scale leap.
Fig. 2 shows the system of closure technologies capable of providing the described development scales.
Here are some examples from bioengineering and artificial life extension technologies as promising areas. In the future, these technologies will be able to extend human life by imparting a mass character to the creation of artificial organs, as well as by introducing biomedical nanobots capable of fixing problem areas of our bodies in the background and non-invasive mode.
For example, Ray Kurzweil predicts,
In 2034, micron-sized artificial blood cells will operate, capable of regulating the optimal state of the blood (controlling clotting) up to 1000 times faster than natural ones. Human trials of nanosubstitutes for leukocytes that do not induce resistance will be conducted. These microorganisms can target specific infections, as well as effectively fight all bacterial, viral and fungal infections and even cancer cells. Nanorobots are capable of destroying pathogenic microorganisms such as harmful bacteria or viruses in 30 seconds. These pathogens break down into harmless amino acids and other nutrients, as opposed to the often toxic waste that is left behind by our immune systems.
Today, using a special microscope in the clinic, you can see how white blood cells destroy bacteria. They very skillfully blocked their escape routes, but this happened very slowly. New nanodevices (2034) do this job in seconds. In addition, they can download software from the Internet, learning about infectious agents that are currently common among people. They can also destroy any artificial pathogens (Kurzweil 2017: 57).

Such dynamics and trends suggest the synthesis of human life with technologies, making their connection inseparable. An additional factor of such a fusion is the embedding of our consciousness into the technological process. We are talking about augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies. Virtual reality in conjunction with the mechanisms of imitation of all human senses (including through blocking and switching of the corresponding zones in the brain) will provide an opportunity for complete immersion in an absolutely constructed new reality. AR technologies will very soon create such conditions that we will live almost all the time in augmented reality, which is a mixture of reality and virtuality. Small tooltips will explain what is happening in the real world and it will be difficult to understand where the true reality ends and the virtual one begins, so closely they will interact.
In this context, it is fundamental to reach such a level of thinking when the need for extremely effective management of the Earth's resources, based on the principle of their non-renewability and irreplaceability, becomes obvious. Thus, the transition to nature-like convergent technologies of the NBICS or NBICS + group will allow building a high-tech architecture so that it is possible to ensure the fulfillment of strategic goals, for example, the development of neighboring planets (their resource base).
Nevertheless, the transformation of both individual and collective consciousness will proceed at an intensive rate. There will be a change in world-view.
Cycles and Waves of World Development
The complexity of the world will show new horizons for the development as soon as the countries enter the sustainable path of the formation of a new high-tech world economic order. That is why, in order to ensure a high-quality crisis-free transit period, there should be the strengthening of the scientific discourse which can be accomplished by intensifying interdisciplinary research, the synthesis of socio-political and natural science research, as well as a purposeful search for key system-forming principles of life/nature (Smirnov 2017: 6–20, 14).
As the most illustrative example of such a process, let us take the cyclical / wave-type principle of the construction of life, which is gaining popularity, but not yet fully understood by very wide circles, including scientific ones. And here we will try to correlate it for completely different sides of reality, giving some examples – from the field of the smallest processes, ‘long distances’ and socio-humanitarian systems. Due to the chosen format of the presentation, space limitations and some other factors of related factors, the main areas of research will be briefly outlined here.
Let us start with the micro, even the nano-world and turn to quantum biology (Al-Khalili and McFadden 2017), through the prism of which we will answer the question: What is a smell? So, the molecular bonds of hydrogen sulfide S – H (the ones for which the smell of rotten eggs is characteristic) vibrate at
a frequency of 76 terahertz (i.e., 76 trillion vibrations per second). Here the principle of oscillation is inherent in nature. It ensures the constant movement of life-forming processes, when a high dynamic is actually hidden behind the external statics, which does not allow life to stand still.
The next in scale is the example of fluctuations and cycles in social processes which shows that global society, like super-large social systems, also has a wave nature. This statement is due to a huge number of factors that determine and affect such a structure of development dynamics. One of the system-forming factors is solar activity which, in particular, is confirmed by a number of studies (e.g., A. L. Chizhevsky, R. Wolf, D. O. Svyatsky, V. Herschel, etc.), not to mention the use of such developments in hedge funds in the exchange game (e.g., with assets related to agriculture).
Thus, the famous American political scholar Arthur M. Schlesinger Jr. published a fundamental monograph on cycles in American history (Schlesinger 1992), in which he focused on substantiating the concept of his father, who discovered the following pattern. In the political life of the United States of the 19th – 20th centuries, the waves of conservatism and liberalism successively succeeded each other. Schlesinger Sr. counted six phases of liberalism, which are characterized by the growth of democracy, and five periods of conservatism, in which democracy remains at the same level. The average fluctuation period is approximately 33 years. Using this scheme, Schlesinger Sr. correctly predicted the results of the elections (change of ruling parties) in 1924, 1939 and 1947, and the forecasts were published not 2–3 months in advance, but 2–3 years before the elections.
According to Schlesinger Jr.,
The era of domination of private interests cannot last forever. Gradually, people get bored with selfish motives and prospects, they get tired of the pursuit of material goods as the highest goal. Entire segments of the population are trapped in the race to acquire. Intellectuals are alienated ... People are beginning to look for meaning in life, not being isolated on themselves. Finally, something that plays the role of a detonator – some problem, grandiose in scale and degree of danger – leads to a breakthrough in a new era in the country's political life (Schlesinger 1992: 49).
In his works, Frank Klinberg, using the methods of content analysis, analyzed a huge number of foreign policy documents and showed that during the extraverted phase, the president dominates the relationship between the President and Congress, whereas during the introverted phase Congress does (Klinberg 1983).
In 1970 American political scientist J. Namenwirth published his research into the pre-election political platforms of the Republican and Democratic parties of the United States. Using content analysis, he analyzed the frequency of use of 73 political categories. His student R. Weber conducted a similar study of the throne speeches of the Queen of England. In both cases, the waves with the periodicity of about 50 years were identified (Namenwirth and Weber 1987).
Scientists have recently done a unique work on the problems of similar global trends, fixing the waves of the so-called positive / negative observed in the English-language literature over a hundred-year period – from 1900 to 2000 (Acerbi et al. 2013). Trends became visible through content analysis of the words ‘mood’, that is, emotionally charged words in English books, using a dataset provided by Google (see Figs 4 and 5).
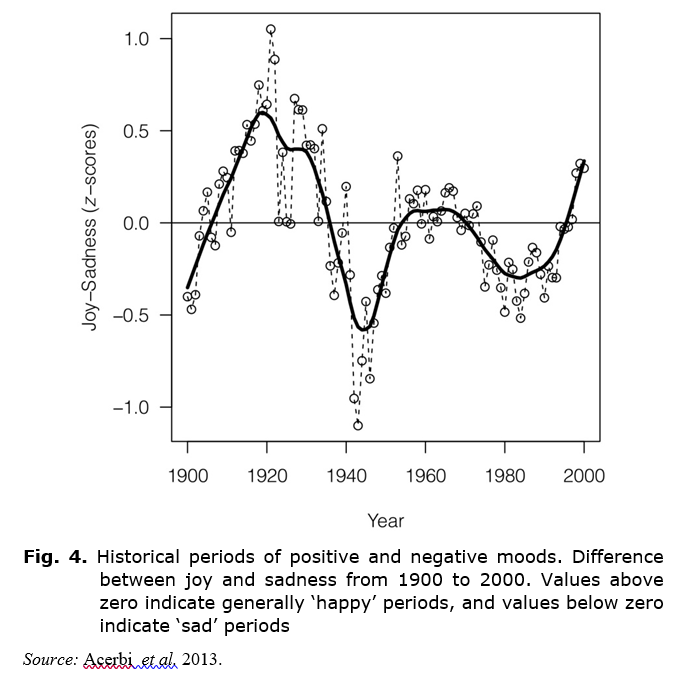
The graph shows the periods of conditional ‘joy’ and ‘sadness’ around the world. The downward trend is explained by an overall decrease in the use of emotion-related words. We clearly see the negativity during World War II as well as around 1980, and a surge of happiness in 1920, 1960, and in 2000.
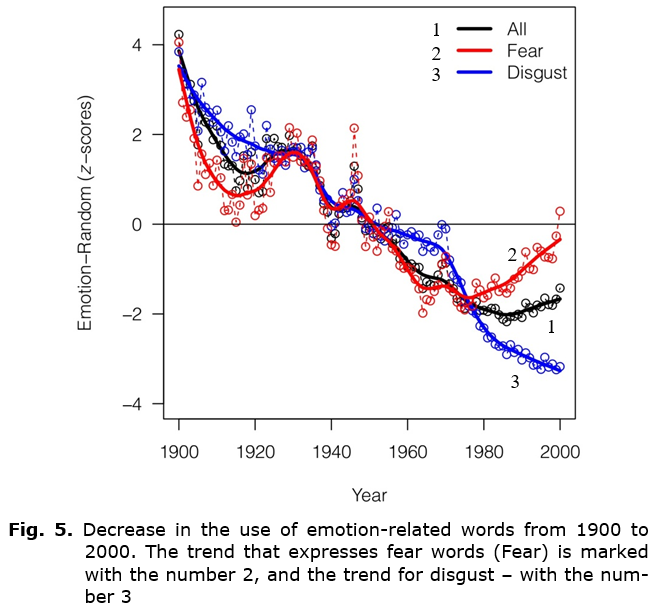
American English used in books has become more ‘emotional’ than British English in the last half century. This is in part the result of a more general stylistic divergence between these two varieties of English (Acerbi et al. 2013; Pocheptsov 2017).
Thus, all of the above examples indicate the wavelike principle of social processes that manifest themselves due to similar tectonic movements in nature. Theoretically, extrapolating such a development into the distant future (inclu-
ding, e.g., through the use of advanced artificial intelligence algorithms and Big Data), the following assumption can be made. Understanding all the multidimensional quantum mechanics of life, all the details and elements, their connections, thereby obtaining a ‘global constructor’, one can predetermine / predict the movement of life into the future and, moreover, up to infinity. However, the dimensions of these processes are amazing in their horizons: 76 trillion vibrations in one molecular bond – versus 45 billion light years of the theoretically expanded universe (i.e., it will take this amount of time for a ray of light to overcome our entire universe).
Here is an example of thinking about different areas of science and life. But what do we need in order to move to a new level of thinking – from a narrow frame thinking one to one that encompasses the laws of life, in order to achieve a truly sustainable and effective universal trajectory of development?
One of the directions is world-system, that is the development of such a sense of reality, when it will be possible to see the system-forming principles of the phenomena of life, for example their interaction in an interdisciplinary field. In this case, the issue of ‘geopolitics’ will be gradually removed from the agenda – in favor of humankind as a single civilization and planet as one ‘spaceship’. And in this case, a new field opens up – a new level of tasks for which humankind must act together.
References
Acerbi A., Lampos V., Garnett P., and Bentley R. A. 2013. The Expression of Emotions in 20th Century Books. PLoS ONE 8(3): e59030. URL: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059030; URL: http://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0059030.
Al-Khalili J., and McFadden J. 2017. Life is on the Brink. Your First Book on Quantum Biology. St. Petersburg: Piter. In Russian (Аль-Халили Дж., МакФадден Дж. Жизнь на грани. Ваша первая книга о квантовой биологии. СПб.: Питер).
Genkin A., and Mikheev A. 2018. Blockchain: How It Works and What Awaits Us Tomorrow. Moscow: Alpina Publisher. In Russian (Генкин А., Михеев А. Блокчейн: Как это работает и что ждет нас завтра. М.: Альпина Паблишер).
Glazyev S. 2018. Leap into the Future. Russia in New Technological and World Economic Paradigms. Moscow: Knizhnyi mir. In Russian (Глазьев С. Ю. Рывок в будущее. Россия в новых технологическом и мирохозяйственном укладах. М.: Книжный мир).
Golovkov A., and Smirnov F. 2017. Saving the Earth's Ecosystem is a New Trend in the Economy of Civilization Development. Intellectual Property Exchange 12: 25–32.
Klinberg F. L. 1983. Cyclical Trends in American Foreign Policy Moods: The Unfolding of America's World Role. N. Y.
Kurzweil R. 2017. Transcend. Nine Steps Towards Eternal Life. Moscow: Mann, Ivanov and Ferber.
Moravec H. 1988. Mind Children: The Future of Robot and Human Intelligence. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Namenwirth J. Z., and Weber R. P. 1987. Dynamics of Culture. Winchester: Alien and Unwin.
Pocheptsov G. 2017. Semantic Wars of Today, or Mental Transformations of Mass Consciousness. Psyfactor. In Russian (Почепцов Г. Смысловые войны сегодняшнего дня, или ментальные трансформации массового сознания. URL: https:// psyfactor.org/lib/sociowar2.htm).
Schlesinger A. M. 1992. Cycles of American History. Moscow: Progress. In Russian (Шлезингер A. M. Циклы американской истории. М.: Прогресс).
Smirnov F. 2011. On the Transformation of Human Consciousness in the Era of Technogenic Globalization. Noviy Universitet ‘Aktualniye Problemy gumanitarnykh i obschestvennykh nauk 4: 28–41. In Russian (Смирнов Ф. О трансформации человеческого сознания в эпоху техногенной глобализации. Новый университет. Серия Актуальные проблемы гуманитарных и общественных наук 4: 28–41).
Smirnov F. 2017. The Theory of World-Systems Analysis (Volume Parameters). Moscow: Narodnoye obrazovaniye. In Russian (Смирнов Ф. Теория мир-системного анализа (параметры объемности). М.: Народное образование).
Smirnov F. 2018. Model for Measuring International Processes: ‘Technology Index’ and the Group of Technologies ‘NBICS +’. Journal Auditor 3(276) (March): 47–54. In Russian (Смирнов Ф. Модель измерения международных процессов: «Индекс технологий» и группа технологий «NBICS+». Аудитор 3(276, март): 47–54).
Smirnov F., and Golovkov A. 2017. Caring for the Earth's Ecology is a Strategy for the Future of Russia and the World. Mir novoi ekonomiki 1: 6–14. In Russian (Смирнов Ф., Головков А. В. Забота об экологии Земли – стратегия будущего России и мира. Мир новой экономики 1: 6–14).
The Global Risks Report 2019. WEF. URL: http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Global_Risks_Report_2019.pdf.
The Global Risks Report 2020. WEF. URL: http://www3.weforum.org/docs/WEF_Global_Risk_Report_2020.pdf.
World Economic Forum. N.d. WEF. URL: www.weforum.org.
[1] URL: https://singularityhub.com/.